The right API protocol can transform how your application performs. I’ve watched countless projects struggle because teams chose protocols based on popularity rather than their actual needs. Whether you’re connecting microservices, building mobile apps, or managing IoT devices, understanding these nine protocols will help you make better architectural decisions.
1. SOAP: The Enterprise Workhorse
SOAP carries the weight of enterprise systems on its XML shoulders. While younger developers sometimes dismiss it as outdated, SOAP continues powering critical systems in banking, healthcare, and government sectors where formal contracts and security aren’t negotiable.
The protocol uses XML-based messaging with strict standards, which makes it verbose but predictable. Built-in WS-Security handles authentication, while ACID compliance ensures transaction reliability. SOAP works over multiple transport protocols including HTTP, SMTP, and TCP.
You’ll find SOAP in banking systems, payment gateways, and legacy enterprise applications. Its comprehensive error handling and strong typing make it reliable, though the verbose XML format and complex implementation can slow development.
2. REST: The Universal Language
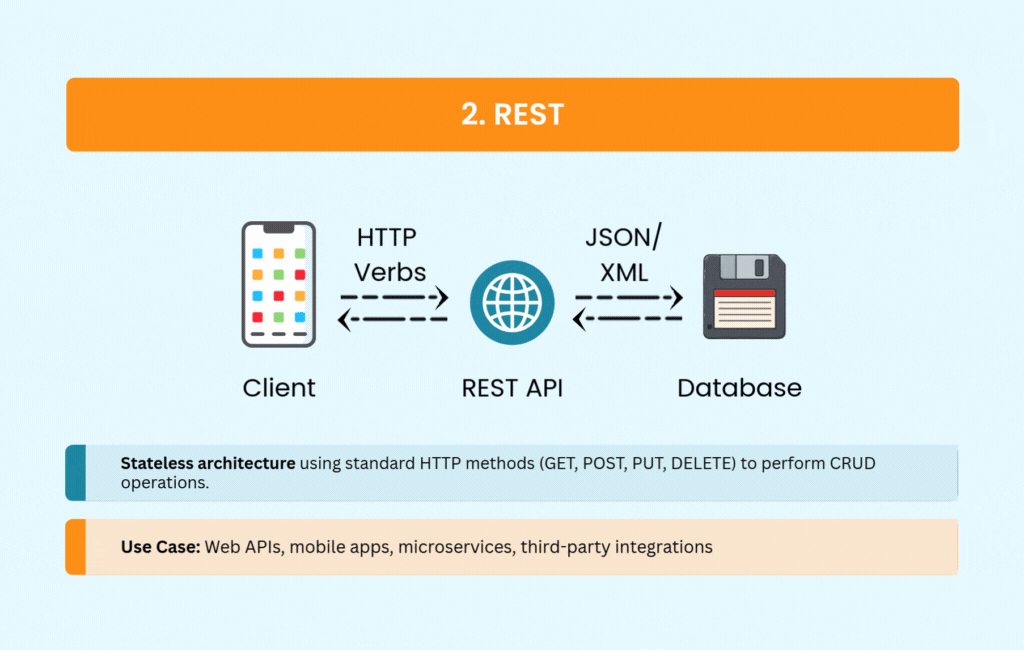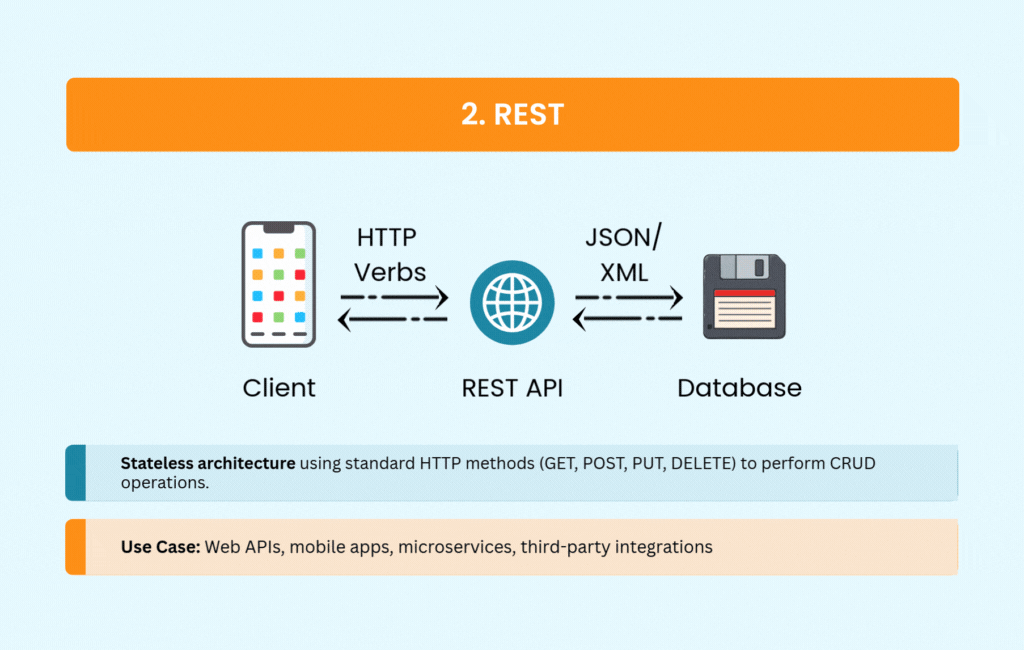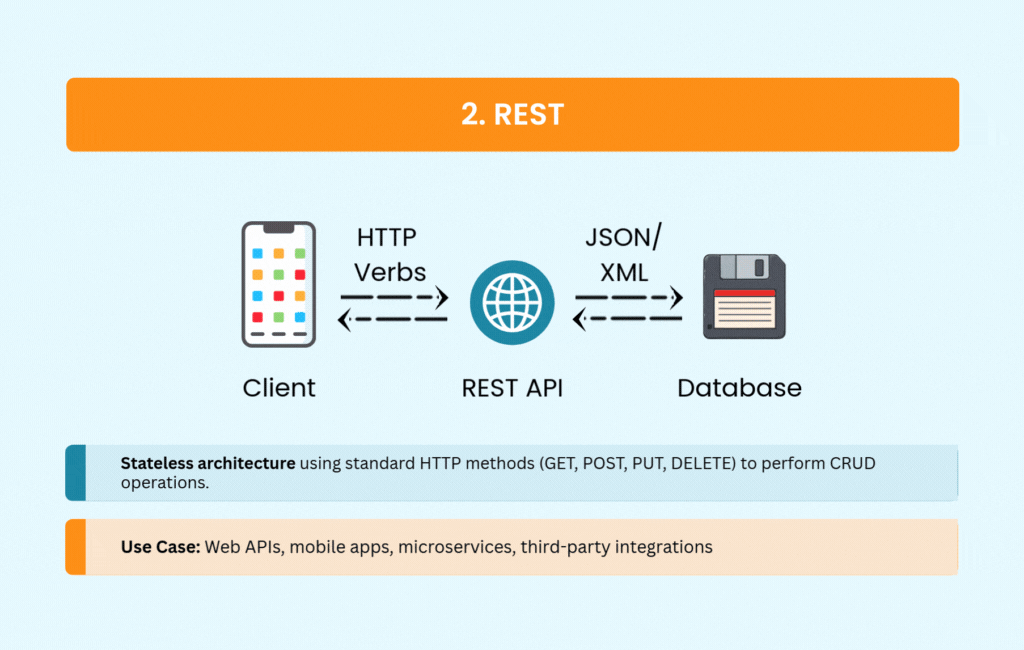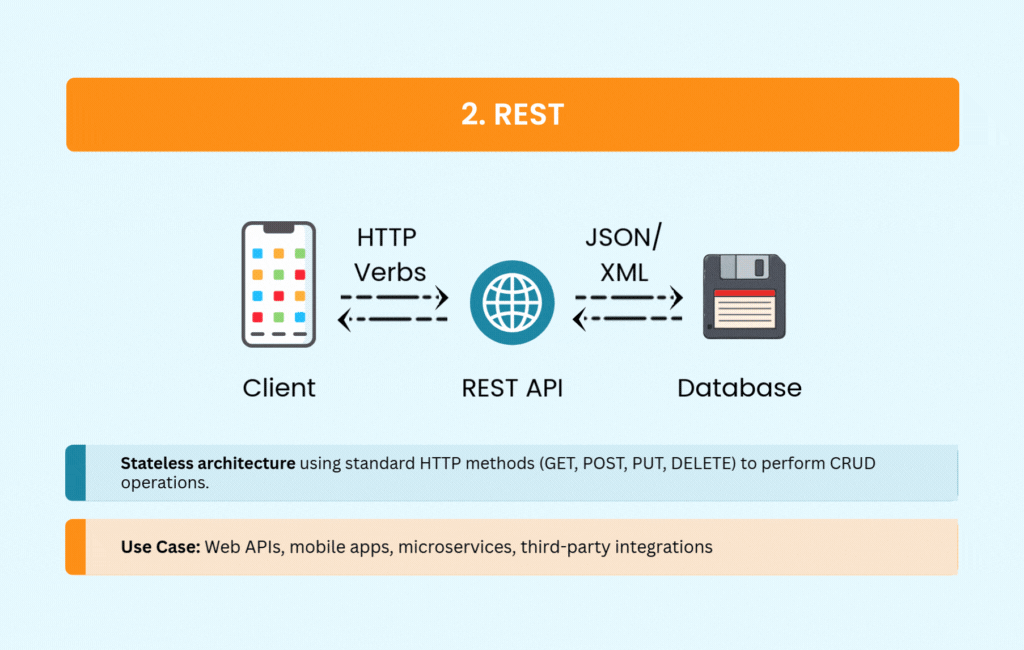
REST became the default choice for web APIs for good reason. It’s straightforward, using standard HTTP methods that most developers already understand. The stateless architecture scales well, and built-in caching mechanisms improve performance without extra work.
REST supports multiple formats, though JSON has become the de facto standard. You’ll see it powering public APIs from Twitter, GitHub, and Stripe, as well as most mobile and web applications. Its simplicity and wide tooling support make it an easy choice for CRUD operations.
The tradeoffs are manageable for most use cases. Over-fetching and under-fetching data can become issues with complex requirements, and REST offers no built-in real-time support. But for straightforward web APIs, REST remains hard to beat.
3. GraphQL: Precision Data Fetching
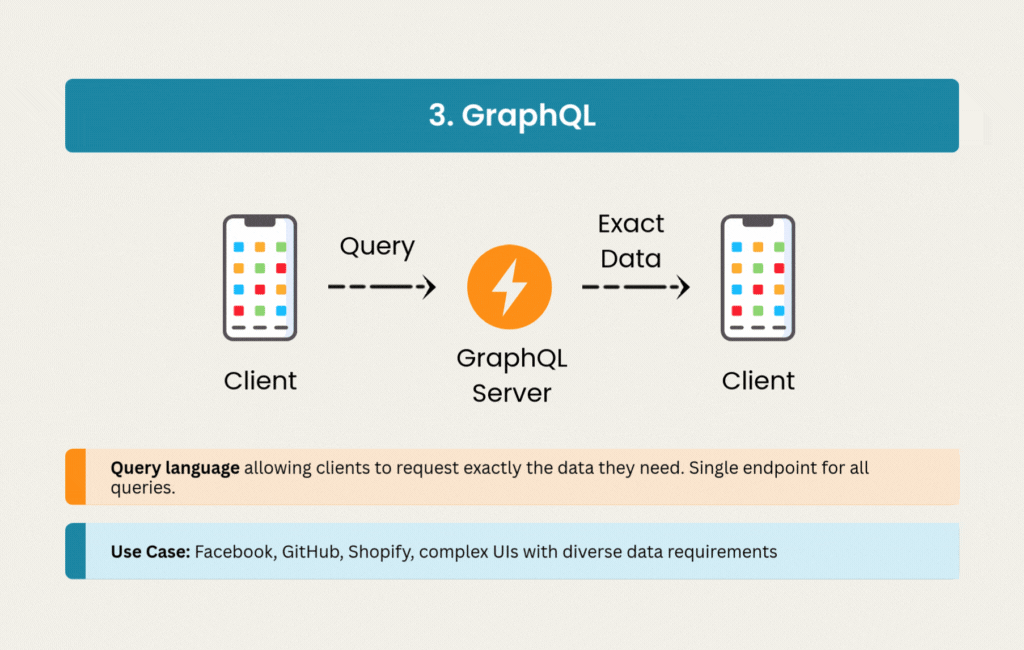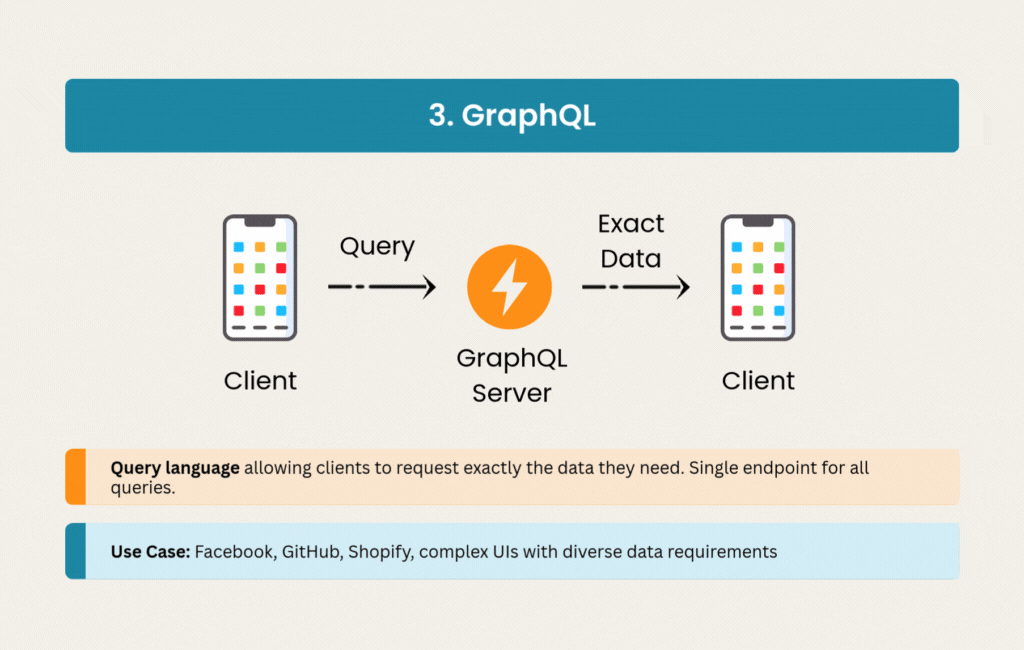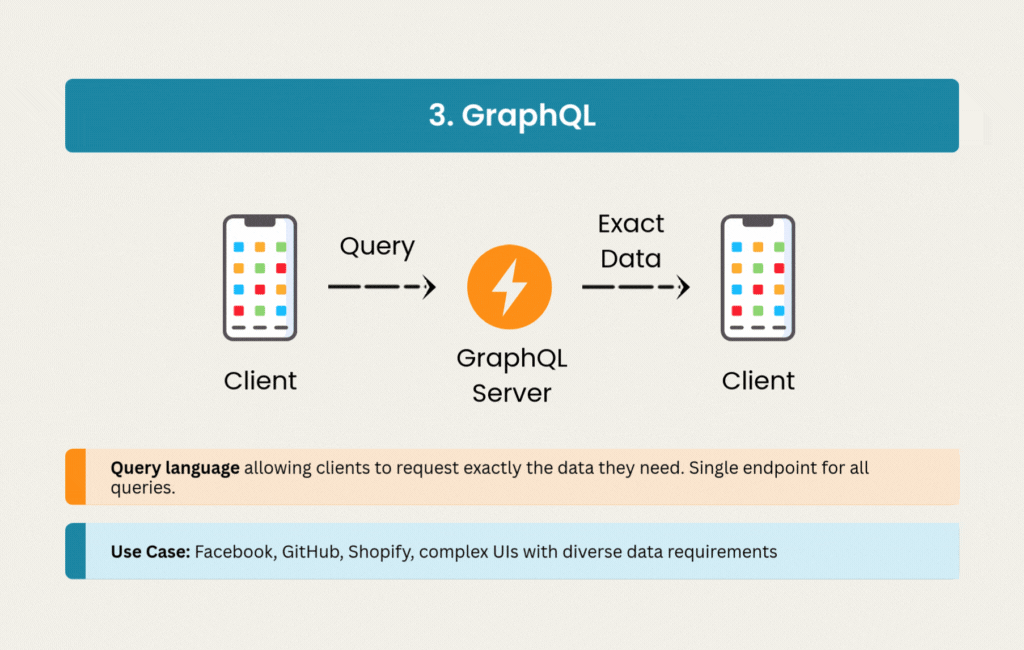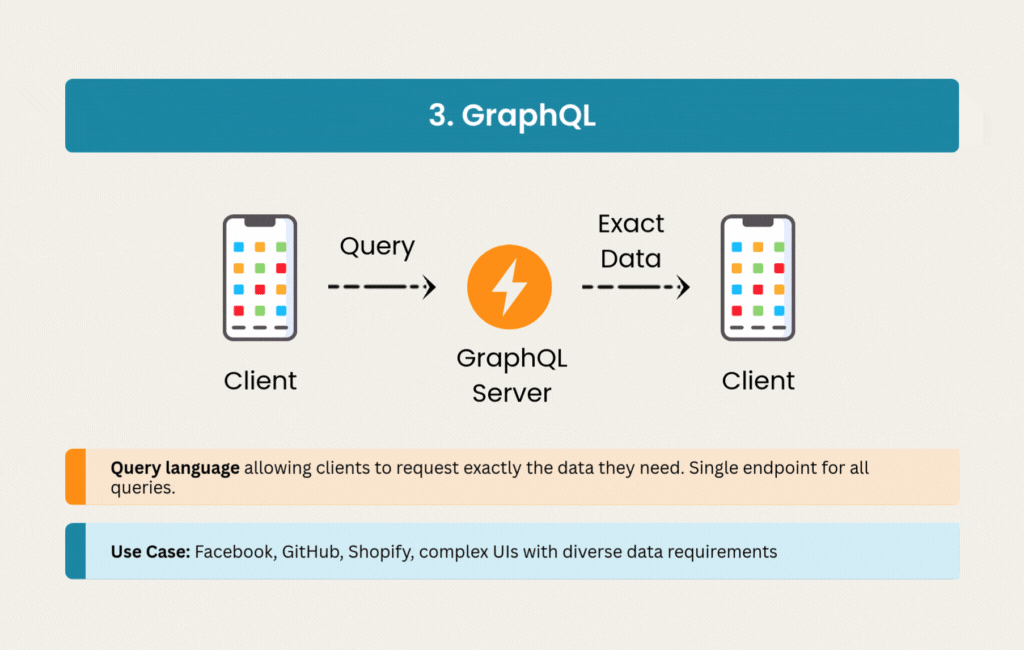
GraphQL emerged from Facebook’s need to efficiently load complex, nested data on mobile devices. Instead of multiple REST endpoints returning fixed data structures, GraphQL provides a single endpoint where clients specify exactly what they need.
The strong typing system generates excellent documentation automatically, and subscriptions enable real-time updates when needed. Social media platforms like Facebook and Instagram rely on GraphQL’s ability to handle complex data requirements across web, mobile, and IoT clients.
The initial setup requires more investment than REST. Caching strategies become more nuanced when clients can request any combination of fields. But for applications battling over-fetching issues or serving multiple client types with different data needs, GraphQL solves real problems.
4. gRPC: Speed for Internal Services
Google built gRPC for the performance demands of internal microservices. Using HTTP/2 and Protocol Buffers for binary serialization, gRPC achieves speeds roughly ten times faster than REST in many scenarios.
HTTP/2 multiplexing allows multiple parallel requests over a single connection, while bidirectional streaming handles complex communication patterns efficiently. The automatic code generation from Protocol Buffer definitions ensures consistency across services in polyglot environments.
gRPC shines in microservices architectures and real-time applications where performance matters. Mobile backends benefit from its efficiency, reducing battery drain. The binary format isn’t human-readable, and browser support remains limited, making gRPC better suited for internal communication than public APIs.
5. WebSocket: Real-Time Conversations
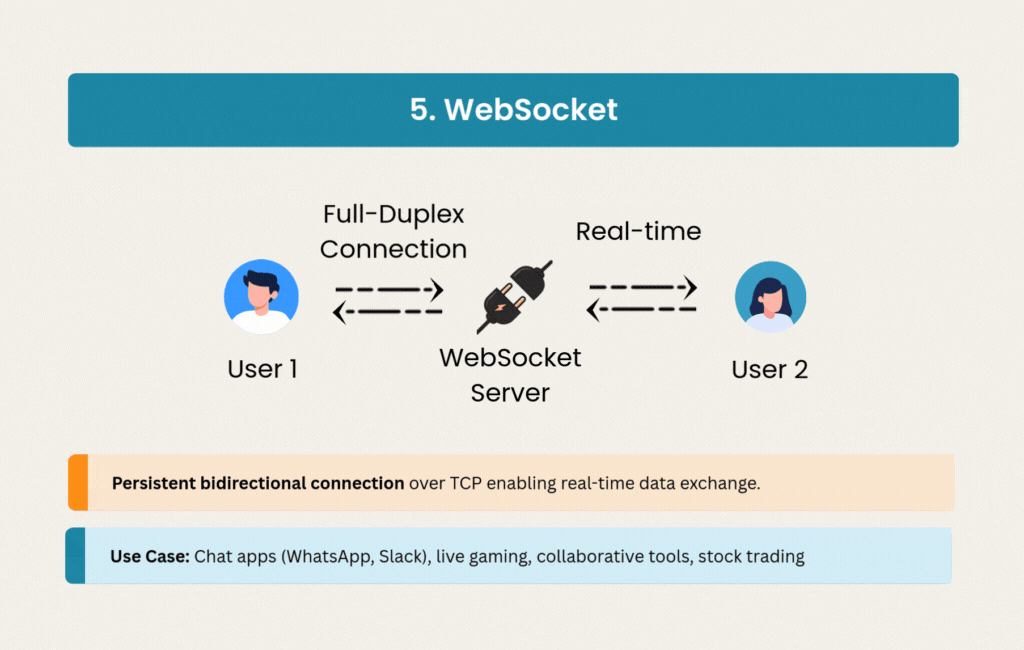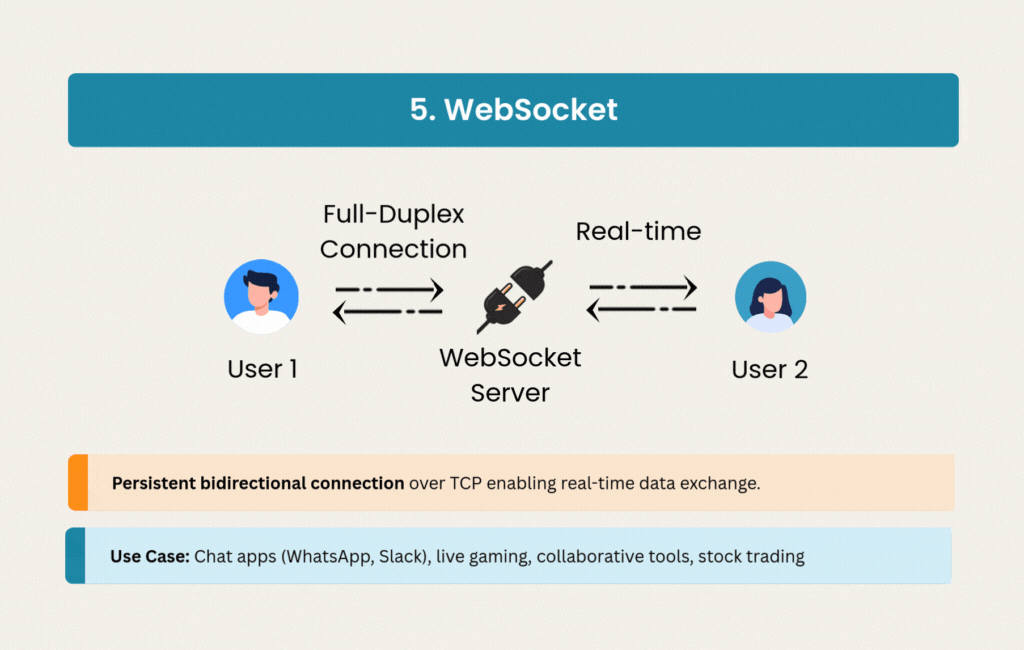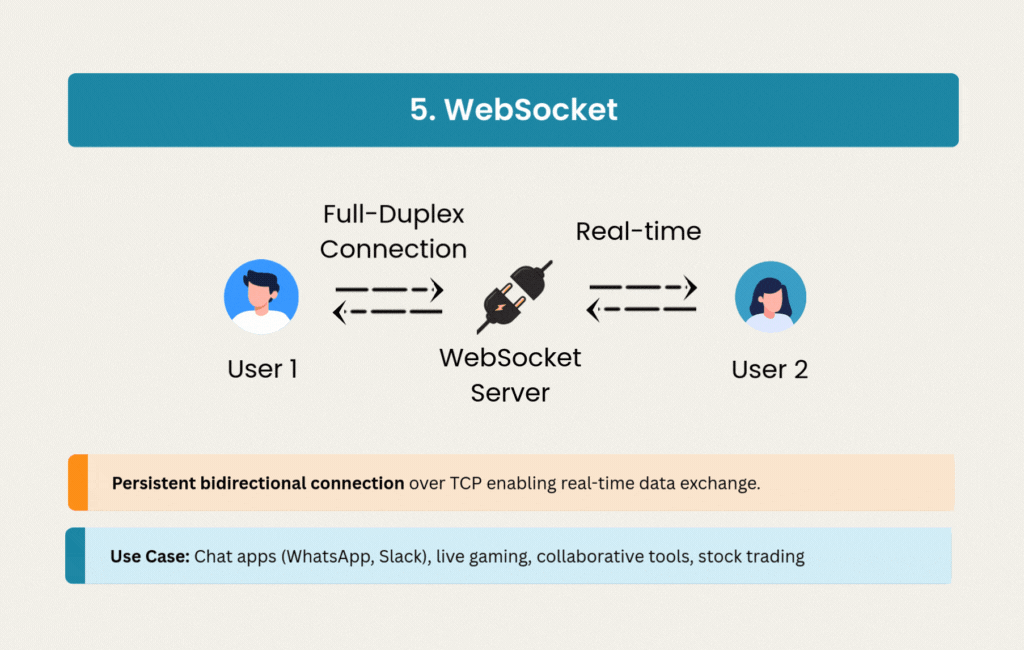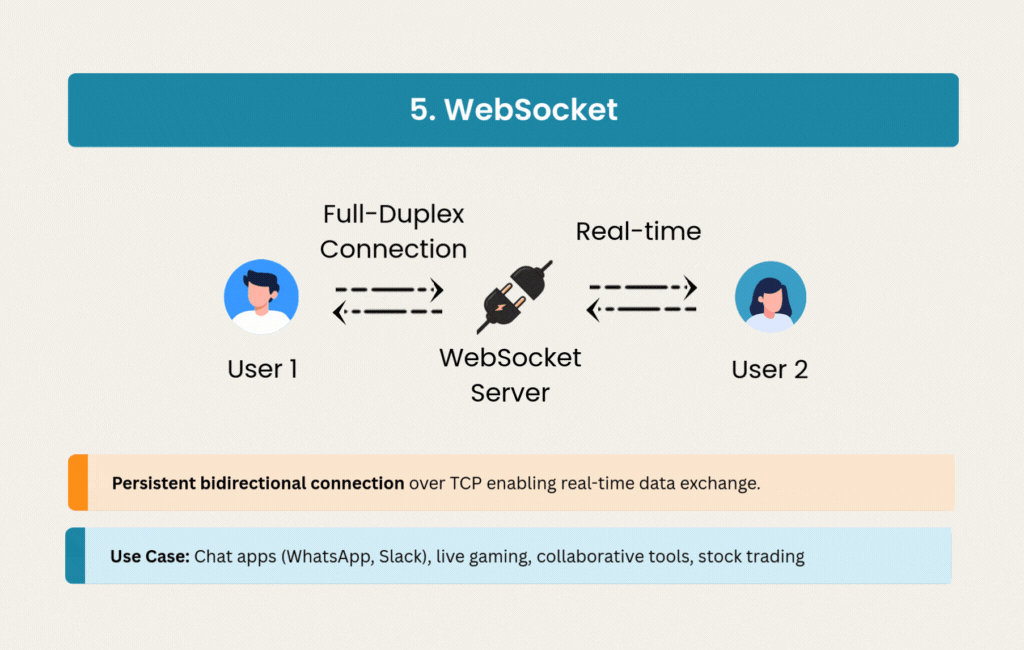
WebSocket opened the door to truly interactive web applications. Instead of polling or other workarounds, WebSocket maintains a persistent, full-duplex connection over TCP with minimal overhead.
Chat applications like WhatsApp, Slack, and Discord depend on WebSocket’s low latency for instant message delivery. Online gaming, collaborative editing tools, and financial trading platforms all need the bidirectional communication that WebSocket provides.
The persistent connections use less bandwidth than repeated HTTP requests, though they introduce scaling challenges. Managing stateful connections requires different infrastructure thinking than stateless REST APIs, but the ability to push data instantly makes WebSocket essential for real-time features.
6. Webhook: Event-Driven Simplicity
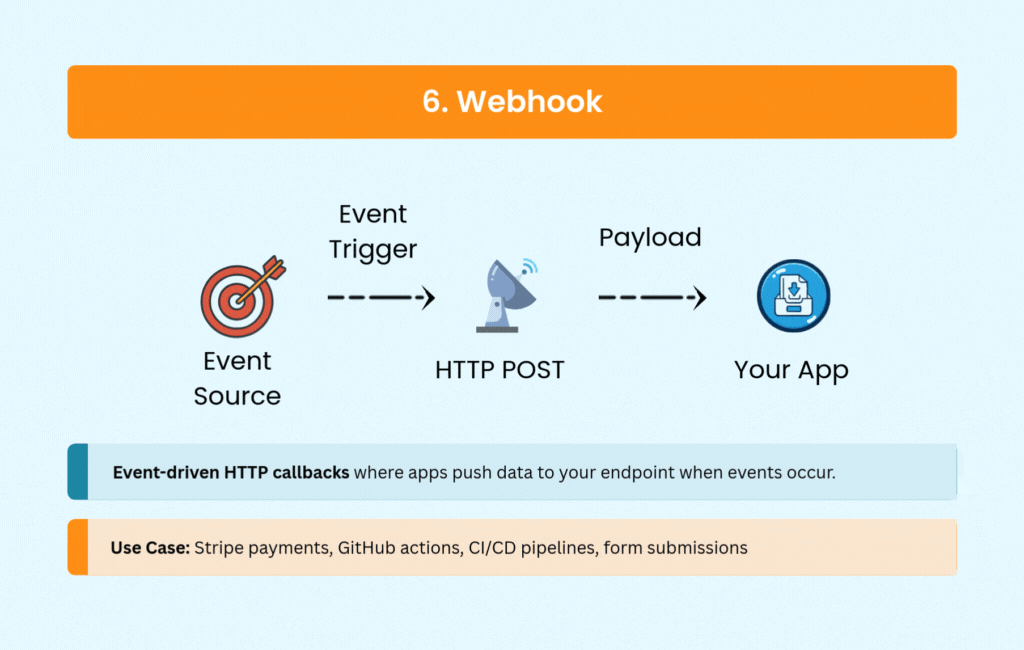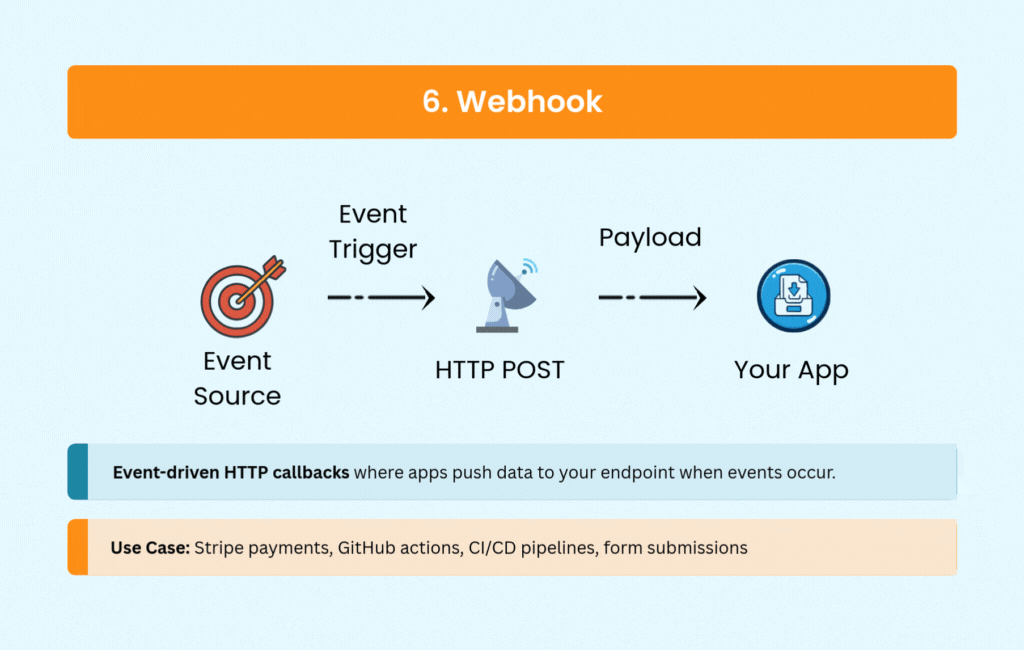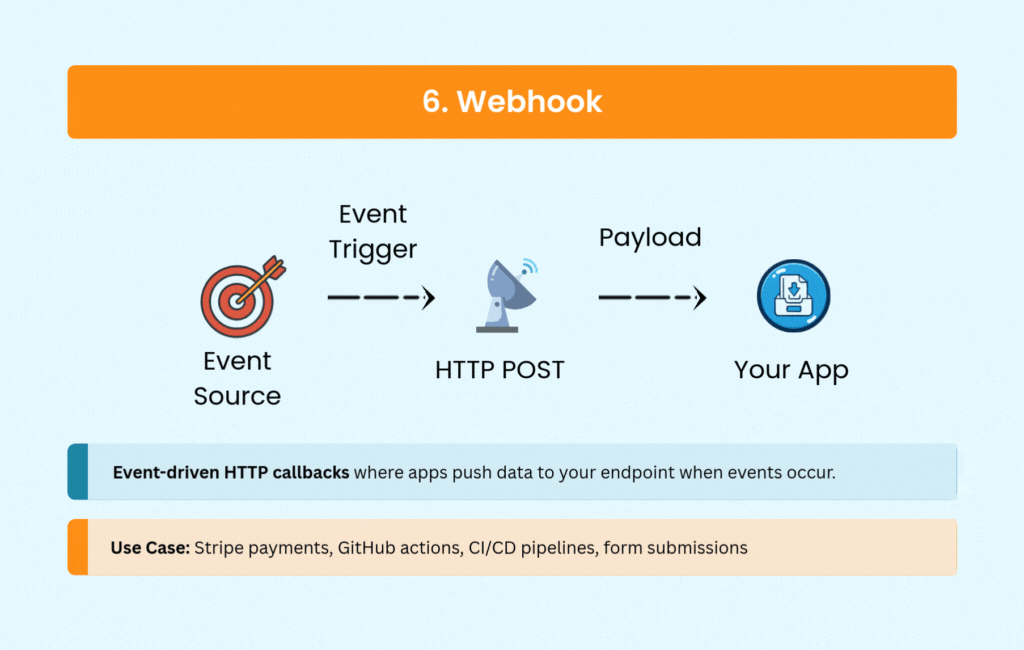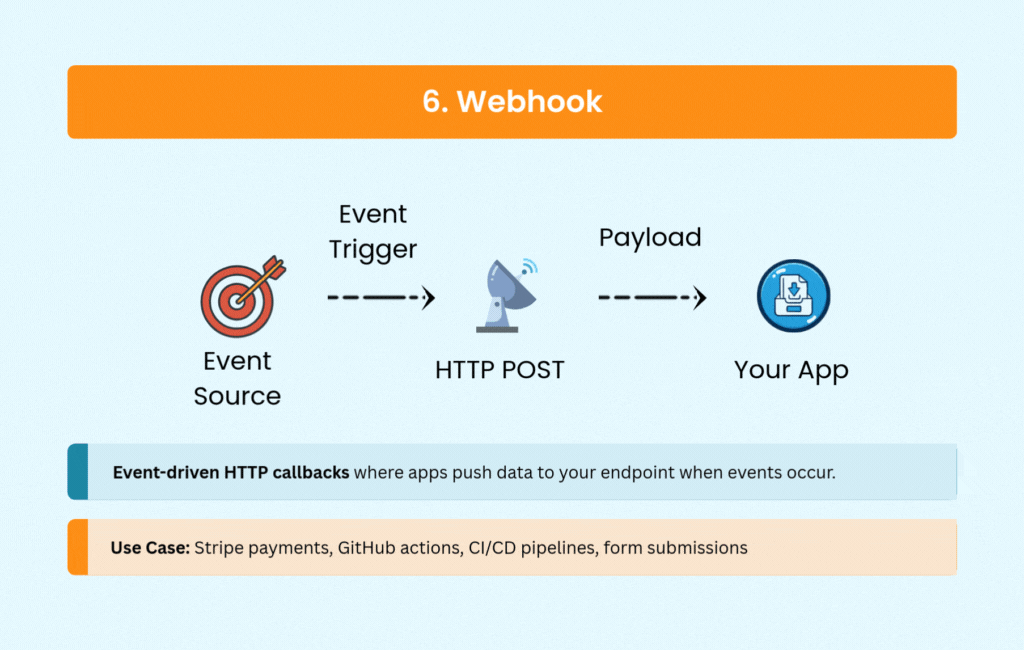
Webhooks flip the communication model. Instead of your application constantly asking if something happened, external services notify you via HTTP POST requests when events occur.
Payment processors like Stripe and PayPal use webhooks to confirm transactions. CI/CD platforms like GitHub and GitLab trigger pipelines through webhooks. E-commerce platforms send order notifications, and CRM systems sync data—all without polling overhead.
The simplicity of webhooks makes them attractive for event-driven architectures. You need a public endpoint to receive notifications and logic to handle retries and potential duplicates, but the real-time updates come with minimal complexity.
7. MQTT: IoT's Lightweight Champion
MQTT was designed for IoT devices operating on unreliable networks with limited bandwidth and battery life. The publish-subscribe pattern with minimal two-byte packet headers makes it incredibly efficient.
Three quality-of-service levels let you balance reliability against resource usage. The Last Will and Testament feature notifies subscribers when a device disconnects unexpectedly, which matters for monitoring remote systems.
Smart home devices, industrial automation, vehicle telemetry, and healthcare monitors rely on MQTT’s lightweight design. It works well on unstable networks and consumes minimal power. Security requires additional implementation, and planning your topic hierarchy carefully prevents future headaches.
8. AMQP: Enterprise Message Reliability
AMQP brings structure and reliability to enterprise messaging. Unlike simple message passing, AMQP provides message queuing with persistence, flexible routing options, and transaction support.
Messages can be routed directly, by topic patterns, or fanned out to multiple consumers. Guaranteed delivery ensures critical messages reach their destination even if services temporarily fail. Financial transactions, order processing systems, and background job queues benefit from these reliability guarantees.
The tradeoffs involve complexity and infrastructure. You need a message broker like RabbitMQ, and the protocol itself is more involved than simpler alternatives. But when message delivery absolutely cannot fail, AMQP’s guarantees justify the investment.
9. JSON-RPC: Blockchain's Simple Protocol
JSON-RPC strips remote procedure calls down to essentials. Using simple JSON encoding, it provides a lightweight, transport-agnostic protocol that’s easy to implement and debug.
Blockchain applications, particularly Ethereum and Bitcoin nodes, standardized on JSON-RPC. Cryptocurrency wallets, embedded systems, and command-line tools benefit from its simplicity. Batch request support improves efficiency when making multiple calls.
The human-readable format makes debugging straightforward, though you miss automatic code generation and sophisticated error handling. For scenarios where simplicity trumps features, JSON-RPC delivers.
Choosing Your Protocol
The decision starts with your requirements, not trends. Need real-time bidirectional communication? WebSocket. Building IoT networks? MQTT. Event-driven notifications? Webhooks. High-performance microservices? gRPC. Complex data requirements? GraphQL. Enterprise security and transactions? SOAP or AMQP. Simple public APIs? REST. Blockchain or lightweight RPCs? JSON-RPC.
Most modern applications use multiple protocols. You might expose REST APIs publicly, connect microservices via gRPC, and handle real-time features through WebSocket. Different problems need different solutions.
Protocol Comparison
Protocol
Speed
Real-time
Complexity
Best For
SOAP
Medium
No
High
Enterprise systems
REST
Fast
No
Low
Web APIs
GraphQL
Fast
Yes*
Medium
Complex queries
gRPC
Very Fast
Yes
Medium
Microservices
WebSocket
Very Fast
Yes
Medium
Chat, gaming
Webhook
N/A
Yes
Low
Events
MQTT
Fast
Yes
Low
IoT
AMQP
Medium
No
High
Message queues
JSON-RPC
Fast
No
Low
Blockchain
*via subscriptions
Protocol
SOAP
Speed
Medium
Real-time
No
Complexity
High
Best For
Enterprise systems
Protocol
REST
Speed
Fast
Real-time
No
Complexity
Low
Best For
Web APIs
Protocol
GraphQL
Speed
Fast
Real-time
Yes*
Complexity
Medium
Best For
Complex queries
Protocol
gRPC
Speed
Very Fast
Real-time
Yes
Complexity
Medium
Best For
Microservices
Protocol
WebSocket
Speed
Very Fast
Real-time
Yes
Complexity
Medium
Best For
Chat, gaming
Protocol
Webhook
Speed
N/A
Real-time
Yes
Complexity
Low
Best For
Events
Protocol
MQTT
Speed
Fast
Real-time
Yes
Complexity
Low
Best For
IoT
Protocol
AMQP
Speed
Medium
Real-time
No
Complexity
High
Best For
Message queues
Protocol
JSON-RPC
Speed
Fast
Real-time
No
Complexity
Low
Best For
Blockchain
Security Fundamentals
Regardless of protocol, security basics remain constant. Encrypt all data in transit with HTTPS/TLS. Implement proper authentication through OAuth 2.0, JWT, or API keys. Validate all inputs to prevent injection attacks. Apply rate limiting to protect against abuse. Monitor usage and maintain logs to detect anomalies. Keep dependencies updated to patch vulnerabilities.
Moving Forward
No single protocol wins every scenario. REST’s popularity stems from its simplicity and broad adoption, not because it’s objectively superior. gRPC excels at internal microservices performance. WebSocket enables real-time interaction. MQTT dominates IoT through efficiency. GraphQL solves specific data fetching problems.
Start with your actual requirements: performance constraints, real-time needs, data complexity, and team capabilities. Prototype when you’re uncertain. Most successful applications combine protocols strategically rather than forcing one solution everywhere.
The best protocol is simply the one that solves your specific problem efficiently.
Frequently Asked Questions
Which protocol is fastest?
gRPC generally performs best for internal communication, while WebSocket excels in real-time scenarios where the persistent connection eliminates handshake overhead.
Should I migrate from REST to GraphQL?
Only if you’re experiencing genuine over-fetching issues or have complex data requirements. REST remains excellent for straightforward CRUD operations.
Is SOAP still relevant?
Yes, particularly in enterprise, financial, and government systems requiring formal contracts and comprehensive security. Legacy systems often depend on it.
Can I use multiple protocols in one application?
Absolutely. Modern applications commonly use REST for public APIs, gRPC for internal microservices, and WebSocket for real-time features.
What's the best protocol for mobile apps?
REST and GraphQL are most common. GraphQL particularly benefits mobile apps by reducing bandwidth usage through precise data fetching.



